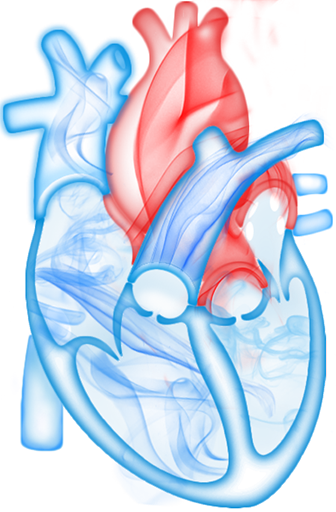Structural heart diseases refer to the pathophysiological changes of the heart caused by anatomical abnormalities in the heart structure, including valvular heart diseases, congenital heart diseases, heart failure, cardiomyopathy and ventricular abnormalities. Among all structural heart diseases, valvular heart diseases are the most prevalent, and most of the structural heart diseases are likely to cause heart failure in the terminal stage.
With the escalating prevalence of structural heart diseases, enhanced patient health awareness, favorable government policies, increased patient affordability, and improved clinical practice of physicians, the interventional medical device market in China had experienced exponential growth in recent years.
-
 Tricuspid Regurgitation
Tricuspid Regurgitation -
 Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Regurgitation -
 Aortic Regurgitation
Aortic Regurgitation -
 Heart Failure
Heart Failure -
 Cardiogenic stroke prevention
Cardiogenic stroke prevention
-
Tricuspid Regurgitation(TR)is caused by the inability of the tricuspid valve to close completely, causing blood to flow from the right ventricle to the right atrium during systole. Chronically, TR results in right-sided congestive heart failure, causing symptoms like peripheral edema, ascites, and hepatic congestion. Approximately 36% of severe tricuspid regurgitation patients die within one year after positive diagnosis. It is expected that by 2030, the number of TTVI Procedures conducted in China and in the world for tricuspid valve diseases will reach approximately 200,900 and 457,800.
-
Mitral Regurgitation (MR) refers to the inability of the mitral valve to close completely, causing blood to flow from the left ventricle into the left atrium during ventricular systole. Studies have indicated that patients diagnosed with severe MR who do not undergo surgery generally have mortality rate of 20% one year following diagnosis and 50% five years following diagnosis. It is expected that by 2030, the number of global TMVI procedures for the treatment of MR will reach approximately 273,200.
-
Aortic Regurgitation (AR) is the incomplete closure of the aortic valve causing backflow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle during diastole. It is expected that by 2030, the number of TAVR procedures for AR will reach approximately 599,400 globally.
-
Heart failure is a complex set of clinical syndromes caused by the changes in myocardial structure and function leading to ventricular ejection and/or low filling. It is a common terminal stage of many heart diseases, and it is also a disease with high morbidity and mortality. It is expected that by 2030, the number of patients with heart failure will reach approximately 39,300,000 globally.
-
Cardiogenic thrombotic stroke is a clinical syndrome in which thrombus from the heart and Aortic arch causes cerebral artery embolism through circulation, resulting in corresponding brain dysfunction.
-
Product Candidates
Product Categories
Verification stage
Feasibility clinical trial
Preparation
Pre-subject enrollment
Completion of the subject enrollments
Clinical trial
Pre-subject enrollment
Completion of the subject enrollments
Completion of clinical trial
Commercialization
-
LuX-ValveTranscatheter tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR) systemChinaGlobal
2023H1
2024H2
-
LuX-Valve PlusTranscatheter tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR) systemChinaGlobal
2023H2
2024H2
-
JensT-ClipTranscatheter tricuspid valve repair (TTVr) systemChinaGlobal
2025H1
2025H2
-
Ken-ValveTranscatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) systemChina2024H1
-
KenFlexTranscatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) systemChina2025H1
-
JensClipTranscatheter mitral valve repair (TMVr) systemChinaGlobal
2024H2
2024H2
-
MitraPatchTranscatheter mitral valve repair (TMVr) systemChinaGlobal
2025H2
2025H2
-
AnchorValveTranscatheter mitral valve replacement (TMVR) systemChina2026H1
-
MicroFluxAtrial septostomy stent & delivery systemChina2024H2
-
AlginSys & EndolnjexMyocardial filling hydrogel & injection systemChina2025H2